Poster session
Poster-presentations of the authors will be posted on 10/20/2021
iA Young Researcher
ID: Hall 17, Report 70
High power terahertz wave emission using DAST crystal
Shizuoka University, ARKRAY Inc., Institute for Molecular Science
(IMS)
In the study, we studied the terahertz wave emitted by DAST crystal
with and without anti reflection coating We found that the power of terahertz wave
generated by DAST crystal with AR coating is higher than the power of terahertz wave generated by
DAST crystal without AR coating
ID: Hall 9, Report
21
Applications for effective representation of imaging with X-ray CT
Shizuoka University
CT allows us to observe the 3D voxel internal structure of an object
but the represent method of CT data is still displaying cross sections in 2D images.
Two representing system by AR and VR are proposed, and these systems allow users to observe the
object at any angle intuitively and confirm the cross-sectional image.
ID: Hall 1, Young Researcher, Report 75
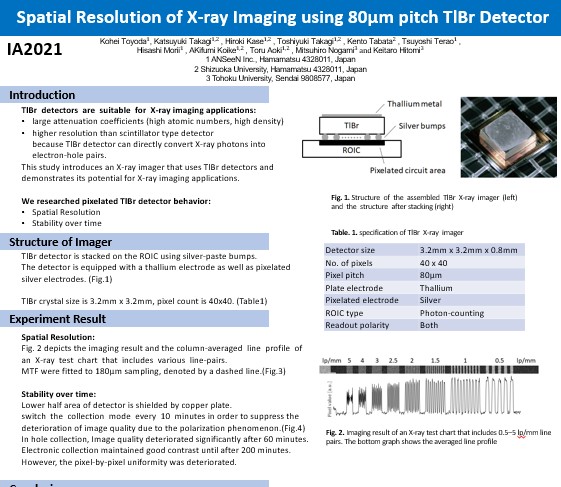
Spatial Resolution of X-ray Imaging using 80µm pitch TlBr Detector
1 ANSeeN Inc., Shizuoka University, Tohoku University
TlBr detector is higher resolution than scintillator type detector
because TlBr detector can directly convert X-ray photons into electron-hole pairs.
We create pixelated TlBr detector for high resolution X-ray imaging.
We researched pixelated TlBr detector behavior such as spatial resolution and stability over time.
Bio- and environmental engineering
ID: Hall 19
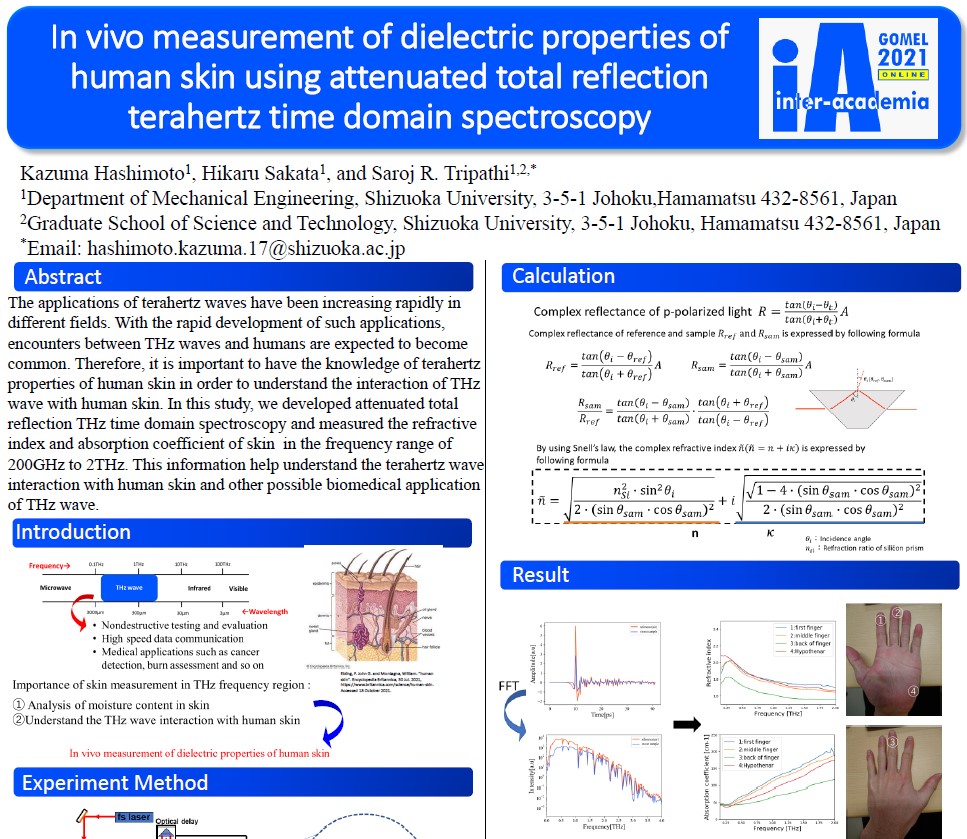
In vivo measurement of dielectric properties of human skin using attenuated total reflection terahertz time domain spectroscopy
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Shizuoka University, 3
The
applications of terahertz waves have been increasing rapidly in
different fields. With the rapid development of such applications,
encounters between THz waves and humans are expected to become
common. Therefore, it is important to have the knowledge of terahertz
properties of human skin in order to understand the interaction of THz
wave with human skin. In this study, we developed attenuated total
reflection THz time domain spectroscopy and measured the refractive
index and absorption coefficient of skin in the frequency range of
200GHz to 2THz. This information help understand the terahertz wave
interaction with human skin and other possible biomedical application
of THz wave.
ID: Hall 20, Report 3
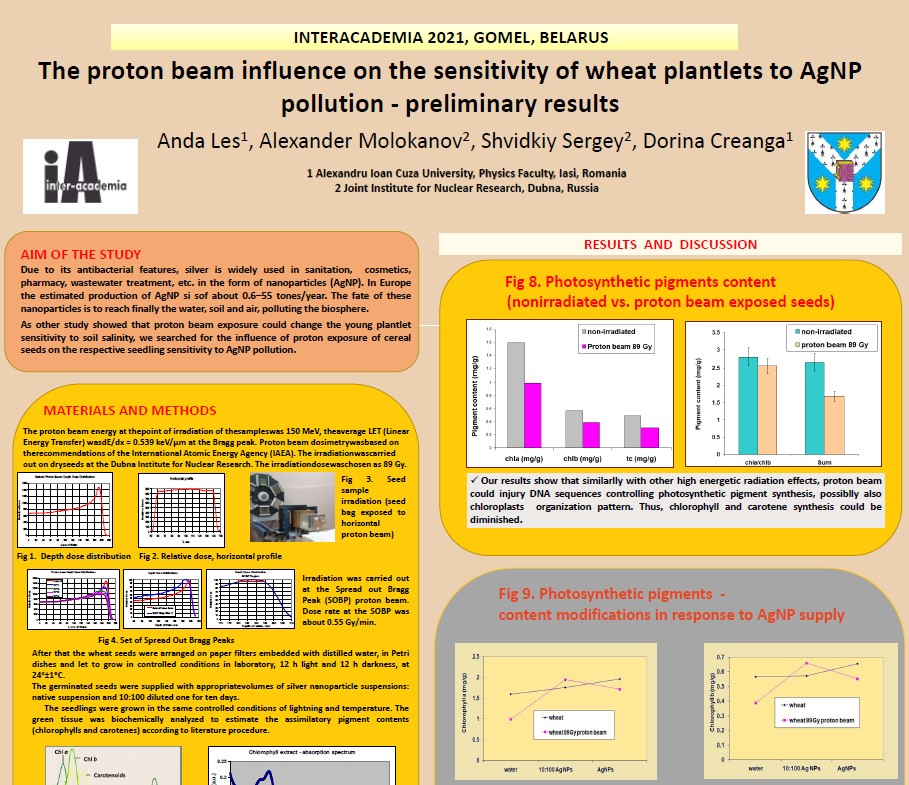
The proton beam influence on the sensitivity of wheat plantlets to AgNP pollution - preliminary results
Alexandru Ioan Cuza University, Joint Institute for Nuclear
Research
We highlight that for the experiments involving seed irradiation
(proton irradiation and AgNP supply), we correlate the quantitative results with other studies
from the literature pointing the
influence of two complementary mechanism of action: harmful free radical generation under the
radiation influence as well as surface microorganism annihilation that eventually protected the
embryos, ensuring a better production of pigments after germination and growth.
Further study will consider antioxidant enzyme assay in control and proton beam exposed samples.
ID: Hall 5, Report 5
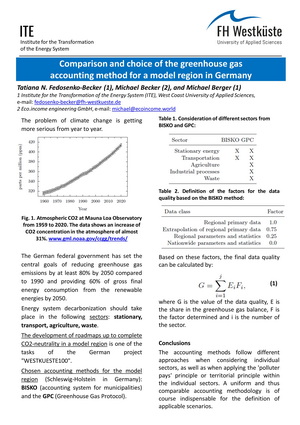
Comparison and choice of the greenhouse gas accounting method for a model region in Germany
Institute for the Transformation of the Energy System (ITE),
West Coast University of Applied Sciences, Eco.income engineering GmbH
Following the sustainable development trends, Germany is
steadily moving towards an energy transformation. This complex process
requires serious planning and an interdisciplinary approach. Within the
framework of the German project "WESTKUESTE100" the roadmaps
to complete CO2-neutrality in a model region will be oered. The rst
step in creating realistic scenarios is to analyze existing accounting methods
of greenhouse gas emissions and to adapt the chosen methods for
the specic purposes. This work describes an approach to the selection
and adaptation of the CO2-equivalent emission accounting method for a
model region in order to create scenarios for the energy transformation.
ID: Hall 4, Report 4
Application of additive technology to create universal carriers of cellular structures
Institute of Chemistry of New Materials of the NAS of Belarus
The work is devoted to obtaining biocompatible carriers with
mechanical properties similar to living tissues by extrusion 3D-printing. Printing of models was
carried out with biocompatible hydrogels of sodium alginate and chitosan in order to determine the
optimal concentrations of components and process parameters.
Electric and Electronic engineering
ID: Hall 12, Report 61
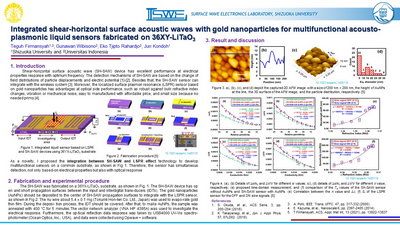
Intergrated shear-horizontal surface acoustic waves with gold nanoparticles for multifunctional acousto-plasmonic liquid sensors fabricated on 36XY-LiTaO3
Shizuoka University and Universitas Indonesia
As a novelty, we proposed the integration between SH-SAW and LSPR
effect technology to develop multifunctional sensors on a common substrate, as shown in Fig 1.
Therefore, the sensor has simultaneous detection, not only based-on electrical properties but also
with optical response.
ID: Hall 5, Report 16
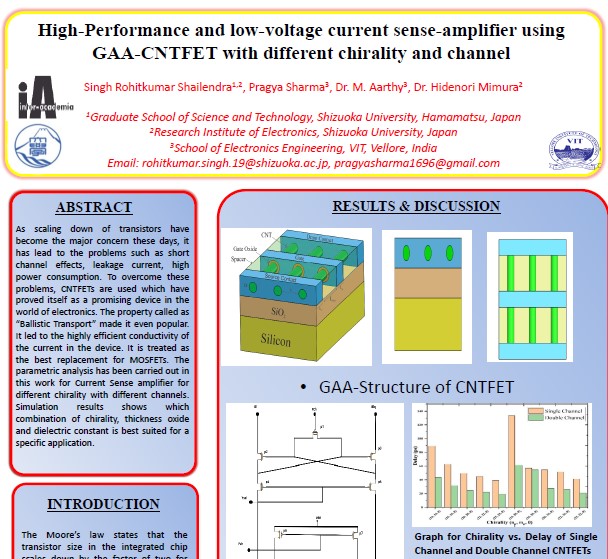
High-Performance and low-voltage current sense-amplifier using GAA-CNTFET with different chirality and channel
Shizuoka University, VIT Vellore
As scaling down of transistors have become the major concern these
days, it has lead to the problems such as short channel effects, leakage current, high power
consumption. To overcome these problems, CNTFETs are used which have proved itself as a promising
device in the world of electronics. The parametric analysis has been carried out in this work for
Current Sense amplifier for different chirality with different channels. Simulation results shows
which combination of chirality, thickness oxide and dielectric constant is best suited for a
specific application.
Internet based education, distance learning
ID: Hall 17, Report 59
Online lesson “Academic English I” for students
Division of Technical Service, Shizuoka university
Academic English I class held in online lecture in 2020 to 2021 and
face to face lecture in 2019.
Manufacturing technology
ID: Hall 6, Report 23
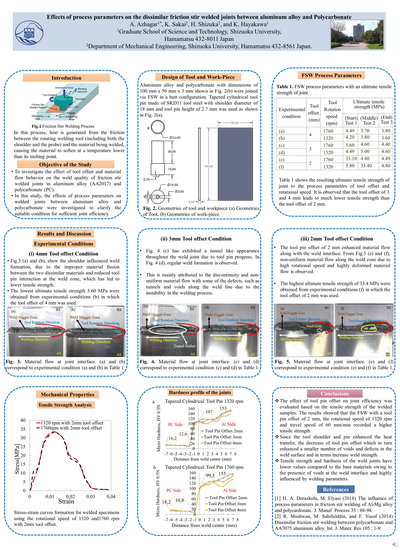
Effects of process parameters on the dissimilar friction stir welded joints between aluminum alloy and Polycarbonate
Shizuoka University
Effects of processing parameters on weld interface and material flow
during friction stir welding of dissimilar materials were investigated. The tapered cylindrical
tool pin made of SKD11 was used to improve the in-process material flow behaviors during the
process.
Material science and technology, smart materials
ID: Hall 9, Report 29
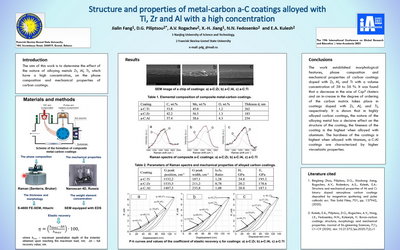
Structure and properties of metal-carbon a-C coatings alloyed with Ti, Zr and Al with a high concentration
Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Francisk Skorina
Gomel State University
The paper presents a comparative analysis of the structure and
mechanical properties of carbon coatings, highly alloyed with metals Ti, Zr and Al. Coatings were
deposited from combined flows of metal and carbon plasma with approximately the same mass content.
Hall 10, Report 35
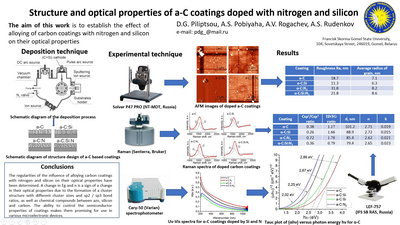
Structure and optical properties of a-C coatings doped with nitrogen and silicon
Francisk Skorina Gomel State University, Belarus
Using a pulsed arc discharge, carbon coatings binary-doped with
silicon
and nitrogen are deposited on quartz and silicon substrates. The structure and phase composition
of
the coatings are studied by atomic force microscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and X-ray photoelectron
spectroscopy. The optic band gap Eg and the refractive index of the coatings are determined
depending
on the alloying elements. The influence of nitrogen and silicon on the formation of the structure
of
the carbon matrix and the formation of chemical compounds in the coatings, leading to a change in
the
width optic band gap Eg, has been established. Changes in the roughness Ra and the size of the
Csp2
cluster are shown in the case of binary doping with nitrogen and silicon.
ID: Hall 12, Report 4
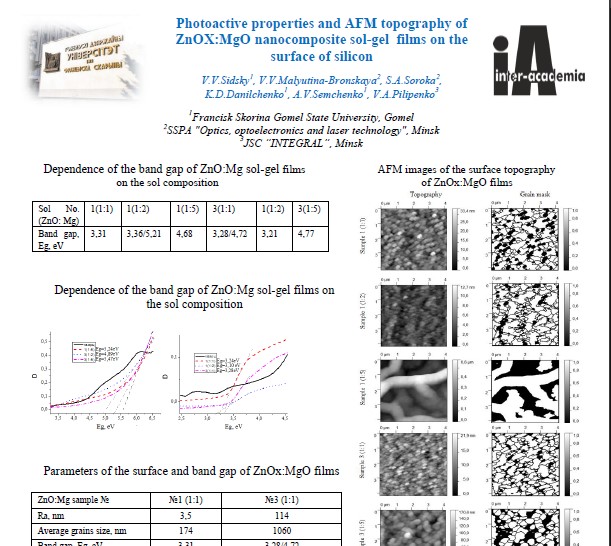
Photoactive properties and AFM topography of ZnOХ:MgO nanocomposite sol-gel films on the surface of silicon
Francisk Skorina Gomel State University
The results of determining by AFM the parameters of sol-gel synthesis
influence for the formation of nanocomposite coatings ZnOх:MgO with a band gap greater than 5 eV
and with high sensitivity to UV and visible radiation are presented. It is shown that depending on
the magnesium concentration change in the surface of the ZnOх: Mg films is observed.
Hall 15, Report 65
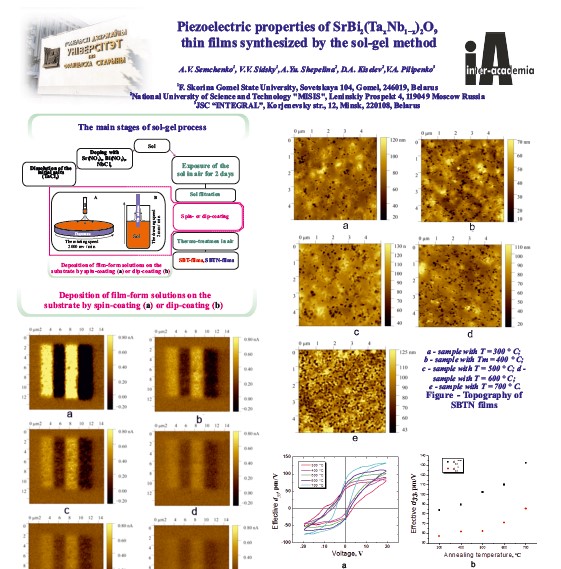
Piezoelectric properties of layers based SrBi2(TaxNb1−x)2O9 synthesized by the sol-gel method
Francisk Skorina Gomel State University
The present work aims to design and study novel functional thin films
with piezoelectrical and multiferroical properties. Thin films of SrBiTa2O9 and SrBi2(TaxNb1−x)2O9
were synthesized by sol-gel method on Pt/Ti/SiO2/Si substrates.
ID: Hall 14, Report 64
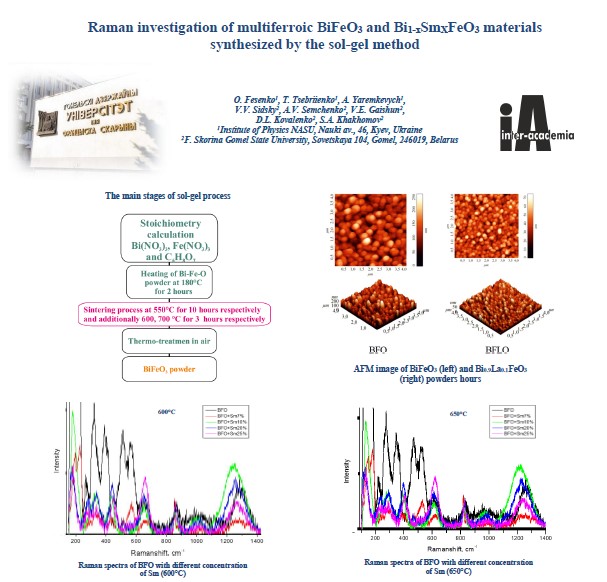
Raman investigation of multiferroic BiFeO3 and Bi1-xSmXFeO3 materials synthesized by the sol-gel method
Francisk Skorina Gomel State University
The present work presents the results of the investigation of
multiferroic materials (BiFeO3 and Bi1-xSmXFeO3) with perovskite structure, which possesses two
types of orderings: ferromagnetic and ferroelectric.
ID: Hall 11, Report 41
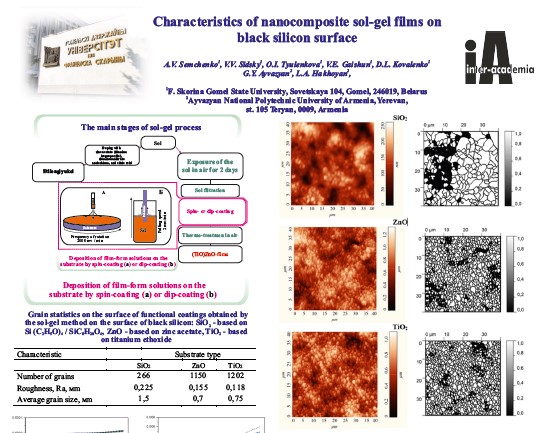
Characteristics of nanocomposite sol-gel films on black silicon surface
Francisk Skorina Gomel State University
The structural and photoelectric characteristics of thin sol-gel ZnO,
TiO2, and SiO2 films on the black silicon (b-Si) surface have been studied. It has been shown that
it is preferable to use ZnO and TiO2 films as passivating and protective films of solar cells
based on b-Si, which have stable structural and optical properties and, at least, do not worsen
the reflection of b-Si in the near infrared and visible regions of the solar radiation.
ID: Hall 11, Report 38
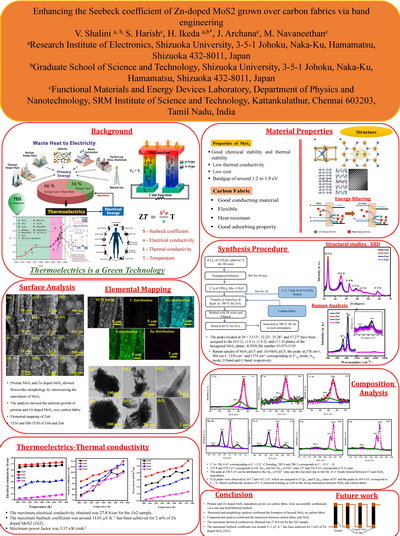
Enhancing the Seebeck coefficient of Zn-doped MoS2 grown over carbon fabrics via band engineering
Shizuoka University, SRM Institute of Science and Technology
Among various 2D materials, molybdenum disulfide semiconductors have
gained much attention in various applications such as electronics, supercapacitors and
optoelectronics due to their unique transport properties. But the nature of charge transport
remains indefinable as they show lower mobility compared to theoretical values. In the present
work, we report a possible method for enhancing the thermoelectric properties of MoS2 by
effectively growing pristine MoS2 and Zn-doped MoS2 on carbon fabrics (CFs) by a simple
hydrothermal method. The uniform growth of pristine MoS2 and Zn-doped MoS2 on CFs was confirmed by
structural and morphological analysis. Various concentrations of Zn doped MoS2 nanosheets grown on
CFs showed significant enhancement thermoelectric performances. It was found that the electrical
conductivity (1.69 x 102 S/cm) was significantly increased for Sample Zn2 with temperature.
ID: Hall 8, Report 26
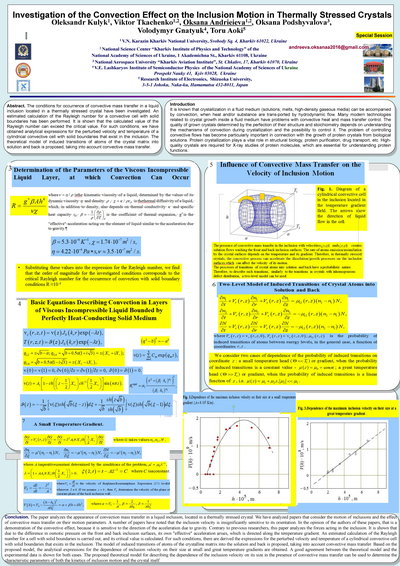
Investigation of the Convection Effect on the Inclusion Motion in Thermally Stressed Crystals
V.N. Karazin Kharkiv National University, National Aerospace
University “Kharkiv Aviation Institute”, Institute of Semiconductor Physics of the National
Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, Shizuoka University
The conditions for occurrence of convective mass transfer in a liquid
inclusion located in a thermally stressed crystal have been investigated. An estimated calculation
of the Rayleigh number for a convective cell with solid boundaries has been performed.
ID: Hall 7, Report 24
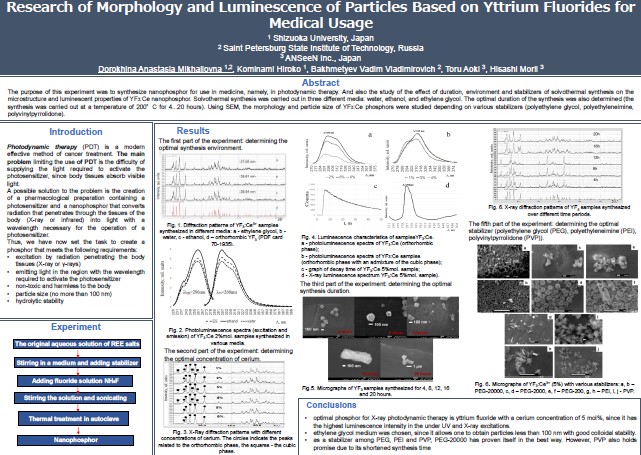
Research of Morphology and Luminescence of Particles Based on Yttrium Fluorides for Medical Usage
Shizuoka University, Saint Petersburg State Institute of
Technology, ANSeeN Inc.
Synthesizing nanophosphor for use in medicine, namely, in
photodynamic therapy. Study of the effect of duration, environment and stabilizers of
sol-vothermal synthesis on the microstructure and luminescent properties of YF3:Ce nanophosphor.
ID: Hall 18, Report 32
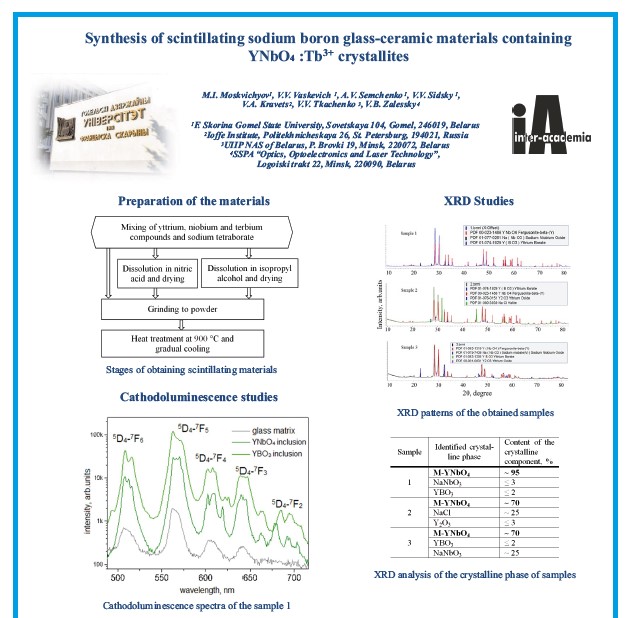
Synthesis of scintillating sodium boron glass-ceramic materials containing YNbO4 :Tb3+ crystallites
Francisk Skorina Gomel State University, SSPA “Optics,
Optoelectronics and Laser Technology”, Ioffe Institute, UIIP NAS of Belarus
The poster shows the stages of obtaining scintillating glass-ceramic
materials containing yttrium niobate activated by terbium ions. The results of XRD analysis and
cathodoluminescence studies of the obtained materials are also presented.
Measurement, identification, and control
ID: Hall 16, Report 57
Investigation of the effect of observation window on the sensitivity enhancement in the multi-pass cell outside the expansion wave tube chamber
Shizuoka University
In this study, the sensitivity enhancement of multi-pass cells in the
inclination of the interior cell window was investigated by calculation using the ray-tracing
method considering laser spread and Snell's law to account for window refraction. As a result, the
higher the sensitivity, the smaller the acceptable range of slope. The inclination tolerance of
the observation window is larger than the inclination toler-ance of the concave mirror.
Metamaterials and metasurfaces
ID: Hall 15, Report 50
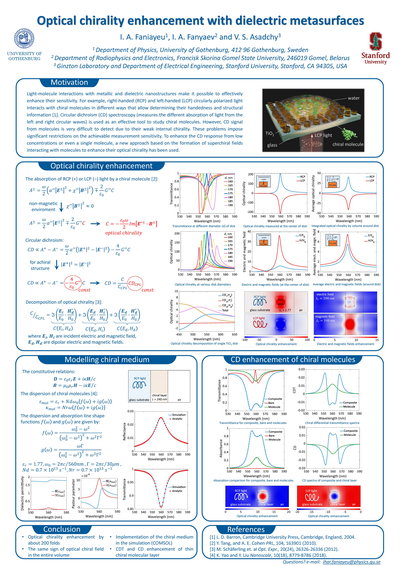
Optical chirality enhancement with dielectric metasurfaces
University of Gothenburg, Francisk Skorina Gomel State
University, Stanford University
We propose the design of an all-dielectric metasurface for an
enhancement of the CD response from chiral molecules with low concentrations. The approach relies
on the formation of superchiral fields interacting with molecules to enhance their optical
chirality.
Nanotechnology and nanometrology
ID: Hall 13, Report 62
Atomic force spectroscopy experiments with amino-functionalized silicon AFM tips and samples
”Alexandru Ioan Cuza” University
he present work uses plasma technology in combination with
wet-chemistry functionalization methods to functionalize silicon atomic force microscopy (AFM)
probe and sample surfaces with amino (-NH2) chemical groups. Plasma cleaning, oxidation, and
hydroxylation processes are used to chemically activate silicon or silicon nitride surfaces by
generating surface silanol (Si-OH) groups. This process is followed by self assembled monolayer
(SAM) deposition of ethanolamine to generate surface amino groups. The amino-functionalized AFM
probes and samples were used in atomic force spectroscopy measurements that confirmed successful
functionalization by chemical force titration.
ID: Hall 16, Report 68
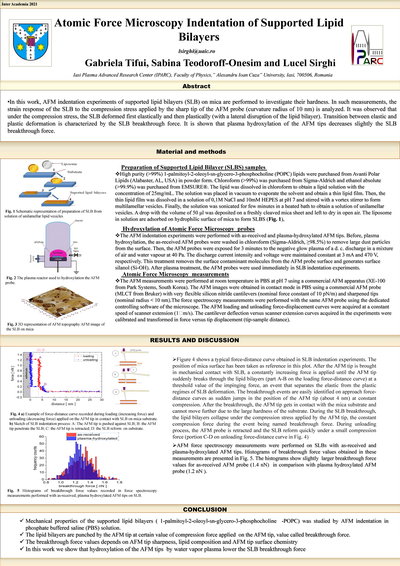
Atomic Force Microscopy Indentation of Supported Lipid Bilayers
”Alexandru Ioan Cuza” University
In this work, AFM indentation experiments of supported lipid bilayers
(SLB) on mica are performed to investigate their hardness. In such measurements, the strain
response of the SLB to the compression stress applied by the sharp tip of the AFM probe (curvature
radius of 10 nm) is analyzed. It was observed that under the compression stress, the SLB deformed
first elastically and then plastically (with a lateral disruption of the lipid bilayer).
Transition between elastic and plastic deformation is characterized by the SLB breakthrough force.
It is shown that plasma hydroxylation of the AFM tips decreases slightly the SLB breakthrough
force.
ID: Hall 6, Report 17
Theoretical study of the impact of a donor-acceptor pair on tunneling current in Si nanodiodes
Shizuoka University
Tunnel diodes are semiconductor devices that operate based on the
band-to-band tunneling (BTBT) mechanism a process that holds promise for future electronics. In
this report we provide a theoretical study of the impact of a donor-acceptor pair on BTBT current,
using a semi-empirical simulation approach and it is found that such a system can enhance the
current and the main factors involved in this enhancement are identified distinctly.
ID: Hall 4, Report 15
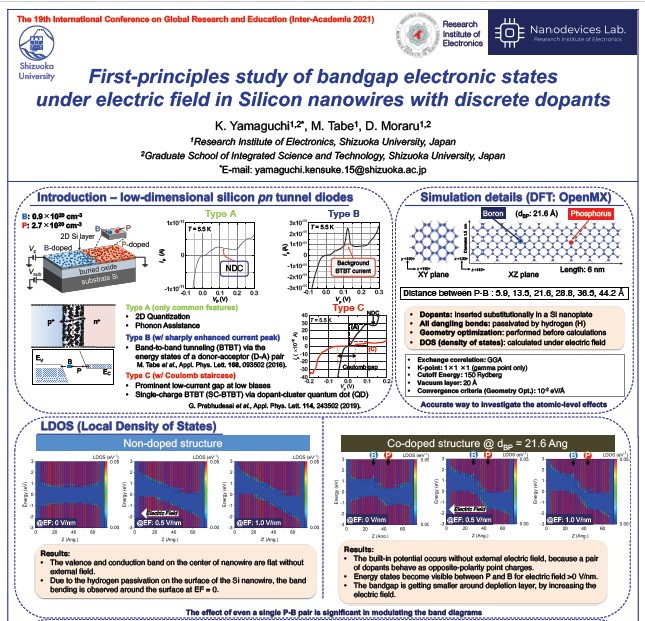
First-principles study of bandgap electronic states under electric field in Silicon nanowires with discrete dopants
Shizuoka University
Low-dimensional Si tunnel diodes show a transport behavior
significantly different compared to conventional (large-scale) devices due to dopant
individuality. In this research work, we aim to understand the role of energy states which can be
induced in the bandgap by the interaction between a donor-atom and an acceptor-atom in Si
nanostructures.
Plasma physics
ID: Hall 14, Report 45
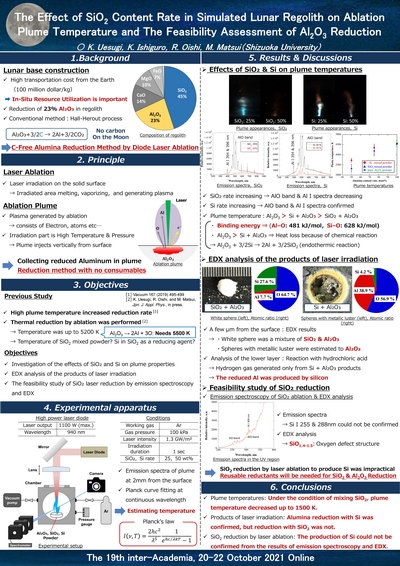
The Effect of SiO2 Content Rate in Simulated Lunar Regolith on Ablation Plume Temperature and The Feasibility Assessment of Al2O3 Reduction
Shizuoka University
We considered the application of lunar regolith for the construction
of a lunar base. To obtain aluminum as building materials, the reduction of simulated lunar
regolith composed of alumina and silicon dioxide was performed using 1-kW-class continuous-wave
diode laser ablation.
ID: Hall 8, Report 20
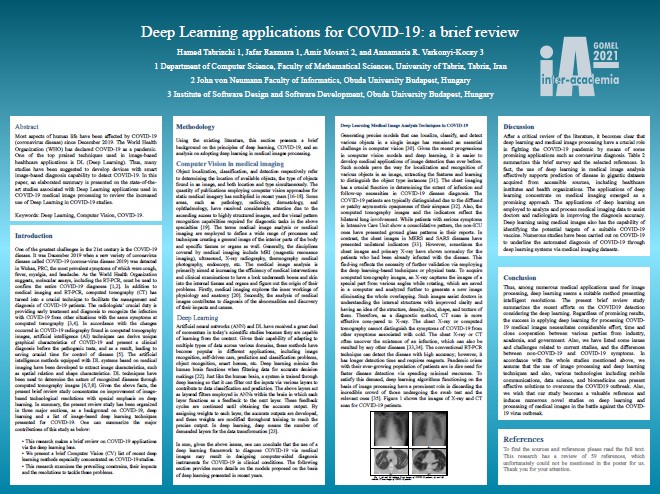
Deep Learning applications for COVID-19: a brief review
University of Tabriz, Obuda University Budapest, Obuda University
Budapest
Most aspects of human life have been affected by COVID-19
(coronavirus disease) since December 2019. The World Health Organization (WHO) has declared
COVID-19 as a pandemic. One of the top praised techniques used in image-based healthcare
applications is DL (Deep Learning). Thus, many studies have been suggested to develop devices with
smart image-based diagnosis capability to detect COVID-19. In this paper, an elaborated summary is
presented on the state-of-the-art studies associated with Deep Learning
applications used in COVID-19 medical image processing to review the increased use of Deep
Learning in COVID-19 studies.